Given that Frontier did an Early Cretaceous Pack and a Late Cretaceous Pack, I thought may be something like that could be done for the Triassic Period. We don't have a lot of species from this time period in the game, so this could be a nice way to get more species from this time period added to the game.
Early Triassic Species Pack
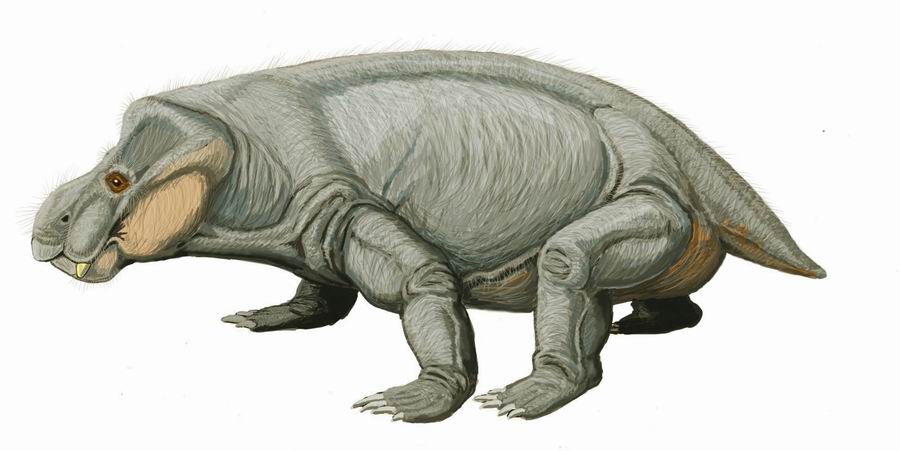
1: Moschorhinus, An extinct genus of therocephalian, it was a carnivorous Synapsid found in the Late Permian to Early Triassic of the South African Karoo Supergroup. It is believed to have hunted like a big cat. They grew to be around 1.5 meters (4.9 feet) long. Moschorhinus were the only large therocephalians. During the Triassic period, they were the largest therocephalians of their time.
or
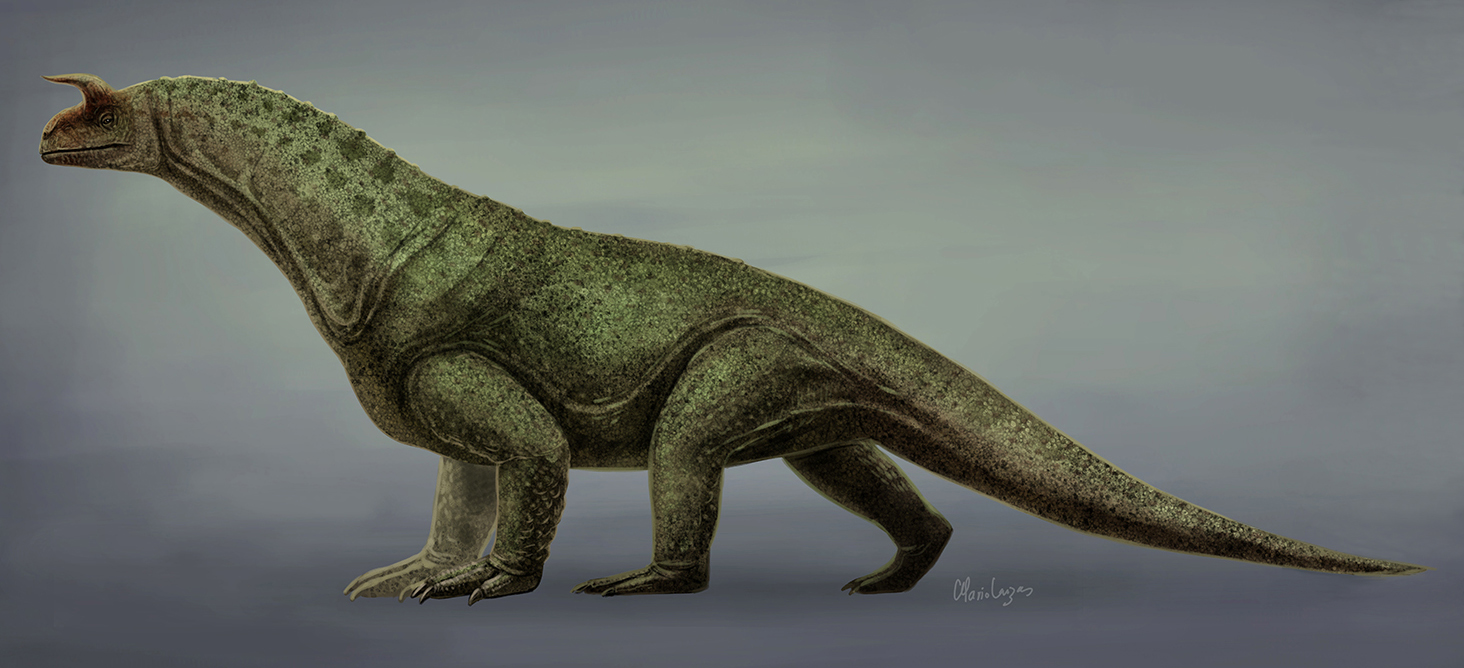
Erythrosuchus, An extinct genus of archosauriform reptiles from the early and middle Triassic period found in the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in the Karoo of South Africa. Erythrosuchus was the largest predator of its time, and was around 4.75–5 meters (15.6–16.4 feet) long. It was the largest erythrosuchid. It was featured in Life on Our Planet.

2: Ordosiodon, An extinct genus of therocephalian therapsids from the Early Triassic found in the Lower Ermaying Formation in Shanxi Province in China. It is known from a partial skull, and skeleton. It is believed to have had a herbivorous diet.

3: Cymbospondylus, A basal early ichthyosaur that lived between the early and middle Triassic period. It could grow between 4 and 17 meters (13-56 feet) long. Cymbospondylus is one of the largest animals known from that time. It appeared in Sea Monsters: A Walking with Dinosaurs Trilogy. Its teeth structure suggest that fed on fish, cephalopods, and possibly other marine reptiles for larger species. If gets added I would recommend the developers have it require fish feeder in its enclosure, but also give the ability to use the shark feeder as well.

or
Aphaneramma, An extinct genus of marine temnospondyl amphibian. It lived during the early Triassic period approximately 240 million years ago. Fossils have been found in the Mianwali Formation of Pakistan, Madagascar, the Zhitkov Formation of Russia, and the Kongressfjellet Formation of Svalbard (Norway). It is believed to have primarily hunted fish.

or
Utatsusaurus: It is the earliest-known ichthyopterygian which lived in the Early Triassic period found in Utatsu-cho, which is part of Minamisanriku-cho, in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan and British Columbia, Canada. It grew to be 2.5–3 meters (8.2–9.8 ft.) long and weighing 57.8 kilograms (127 lb.). It is believed to have primarily fed on fish.
4: Thrinaxodon, An extinct genus of cynodonts lived in what are now South Africa and Antarctica during the early Triassic period. It was roughly the size of a fox and possibly covered in hair. It's teeth structure suggests it fed on insects, invertebrates, and small herbivores. Its generic name was taken from the Ancient Greek for "trident tooth", thrinax and odon. The specific name is Latinised Greek for "smooth-nosed". It appeared in the Walking with Dinosaurs series.

Late Triassic Species Pack
1: Lisowicia, An extinct genus of giant dicynodont synapsid that lived in what is now Poland during the late Triassic period. Lisowicia is the largest known dicynodont, as well as the largest non-mammalian synapsid, and is estimated to have weighed between 5–6 tons, comparable in size to modern elephants. It was also one of the last dicynodonts, living shortly before their extinction at the end of the Triassic period. Lisowicia is unique amongst dicynodonts for its erect posture, with all four limbs held upright directly under its body. This is similar to the limbs of living mammals and dinosaurs, but unlike the sprawling and semi-erect postures typical of all other dicynodonts (and indeed all other non-mammalian synapsids), and shares many independently evolved features of its limbs with large mammals.

2: Plateosaurus, A genus of plateosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period, around 214 to 204 million years ago, in what is now Central and Northern Europe. Adults of this species grew between 4.8 to 10 meters (16 to 33 feet) in length, and ranged in mass from 600 to 4,000 kilograms (1,300 to 8,800 lb.). These animals are believed to have lived for at least 12 to 20 years, but the maximum life span is not known. The oldest individual found was around 27 years of age and was still growing. The meaning of its name is not clearly understood. In 1846, a geologist speculated that "(πλᾰτῠ́ς, breit)" [English: broad] was the origin of the name, German paleontologist believed its name was derived from the stem of πλᾰτέος (plateos), the genitive case of the masculine adjective platys in Ancient Greek. In the same year, another researcher proposed that the name derives from the Ancient Greek πλατη (platê – "paddle", "rudder"; the researcher translates this as Latin pala = "spade") and σαυρος (sauros – "lizard").
or
Riojasaurus, A herbivorous sauropodomorph dinosaur named after La Rioja Province in Argentina where it was found in the Los Colorados Formation in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin that lived during the late Triassic period. Riojasaurus is the only known riojasaurid to live in South America. It is estimated to have grown between 6.6 and 10 meters (22-33 ft.) and its weight between 800 kilograms and 3 metric tons (1,800 lb. and 3.3 short tons). Unfortunately, in 1994, 56 caudal vertebrae from one specimen, and a cast of the skull of Riojasaurus incertus, along with several other specimens, were stolen from the National University of La Rioja in Argentina, which have still not been found.

3: Tanystropheus, An extinct genus of archosauromorph reptile which lived during the Triassic Period in Europe, Asia, and North America. Tanystropheus is one of the most well-described non-archosauriform archosauromorphs, known from numerous fossils, including nearly complete skeletons. Some species within the genus may have reached a total length of 6 meters (20 feet), making Tanystropheus the longest non-archosauriform archosauromorph as well. Its genus name means long hinged.

4: Raeticodactylus, A genus of non-pterodactyloid pterosaur from the late Triassic lower Kössen Formation (about 213-209 million years ago) of the central Austroalpine of Grisons, Switzerland. It had a wingspan of 4.41 feet. It has been debated whether it was a piscivore or omnivore.

Early Triassic Species Pack
1: Moschorhinus, An extinct genus of therocephalian, it was a carnivorous Synapsid found in the Late Permian to Early Triassic of the South African Karoo Supergroup. It is believed to have hunted like a big cat. They grew to be around 1.5 meters (4.9 feet) long. Moschorhinus were the only large therocephalians. During the Triassic period, they were the largest therocephalians of their time.
or
Erythrosuchus, An extinct genus of archosauriform reptiles from the early and middle Triassic period found in the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in the Karoo of South Africa. Erythrosuchus was the largest predator of its time, and was around 4.75–5 meters (15.6–16.4 feet) long. It was the largest erythrosuchid. It was featured in Life on Our Planet.
2: Ordosiodon, An extinct genus of therocephalian therapsids from the Early Triassic found in the Lower Ermaying Formation in Shanxi Province in China. It is known from a partial skull, and skeleton. It is believed to have had a herbivorous diet.
3: Cymbospondylus, A basal early ichthyosaur that lived between the early and middle Triassic period. It could grow between 4 and 17 meters (13-56 feet) long. Cymbospondylus is one of the largest animals known from that time. It appeared in Sea Monsters: A Walking with Dinosaurs Trilogy. Its teeth structure suggest that fed on fish, cephalopods, and possibly other marine reptiles for larger species. If gets added I would recommend the developers have it require fish feeder in its enclosure, but also give the ability to use the shark feeder as well.
or
Aphaneramma, An extinct genus of marine temnospondyl amphibian. It lived during the early Triassic period approximately 240 million years ago. Fossils have been found in the Mianwali Formation of Pakistan, Madagascar, the Zhitkov Formation of Russia, and the Kongressfjellet Formation of Svalbard (Norway). It is believed to have primarily hunted fish.
or
Utatsusaurus: It is the earliest-known ichthyopterygian which lived in the Early Triassic period found in Utatsu-cho, which is part of Minamisanriku-cho, in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan and British Columbia, Canada. It grew to be 2.5–3 meters (8.2–9.8 ft.) long and weighing 57.8 kilograms (127 lb.). It is believed to have primarily fed on fish.
4: Thrinaxodon, An extinct genus of cynodonts lived in what are now South Africa and Antarctica during the early Triassic period. It was roughly the size of a fox and possibly covered in hair. It's teeth structure suggests it fed on insects, invertebrates, and small herbivores. Its generic name was taken from the Ancient Greek for "trident tooth", thrinax and odon. The specific name is Latinised Greek for "smooth-nosed". It appeared in the Walking with Dinosaurs series.
Late Triassic Species Pack
1: Lisowicia, An extinct genus of giant dicynodont synapsid that lived in what is now Poland during the late Triassic period. Lisowicia is the largest known dicynodont, as well as the largest non-mammalian synapsid, and is estimated to have weighed between 5–6 tons, comparable in size to modern elephants. It was also one of the last dicynodonts, living shortly before their extinction at the end of the Triassic period. Lisowicia is unique amongst dicynodonts for its erect posture, with all four limbs held upright directly under its body. This is similar to the limbs of living mammals and dinosaurs, but unlike the sprawling and semi-erect postures typical of all other dicynodonts (and indeed all other non-mammalian synapsids), and shares many independently evolved features of its limbs with large mammals.
2: Plateosaurus, A genus of plateosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period, around 214 to 204 million years ago, in what is now Central and Northern Europe. Adults of this species grew between 4.8 to 10 meters (16 to 33 feet) in length, and ranged in mass from 600 to 4,000 kilograms (1,300 to 8,800 lb.). These animals are believed to have lived for at least 12 to 20 years, but the maximum life span is not known. The oldest individual found was around 27 years of age and was still growing. The meaning of its name is not clearly understood. In 1846, a geologist speculated that "(πλᾰτῠ́ς, breit)" [English: broad] was the origin of the name, German paleontologist believed its name was derived from the stem of πλᾰτέος (plateos), the genitive case of the masculine adjective platys in Ancient Greek. In the same year, another researcher proposed that the name derives from the Ancient Greek πλατη (platê – "paddle", "rudder"; the researcher translates this as Latin pala = "spade") and σαυρος (sauros – "lizard").
or
Riojasaurus, A herbivorous sauropodomorph dinosaur named after La Rioja Province in Argentina where it was found in the Los Colorados Formation in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin that lived during the late Triassic period. Riojasaurus is the only known riojasaurid to live in South America. It is estimated to have grown between 6.6 and 10 meters (22-33 ft.) and its weight between 800 kilograms and 3 metric tons (1,800 lb. and 3.3 short tons). Unfortunately, in 1994, 56 caudal vertebrae from one specimen, and a cast of the skull of Riojasaurus incertus, along with several other specimens, were stolen from the National University of La Rioja in Argentina, which have still not been found.
3: Tanystropheus, An extinct genus of archosauromorph reptile which lived during the Triassic Period in Europe, Asia, and North America. Tanystropheus is one of the most well-described non-archosauriform archosauromorphs, known from numerous fossils, including nearly complete skeletons. Some species within the genus may have reached a total length of 6 meters (20 feet), making Tanystropheus the longest non-archosauriform archosauromorph as well. Its genus name means long hinged.
4: Raeticodactylus, A genus of non-pterodactyloid pterosaur from the late Triassic lower Kössen Formation (about 213-209 million years ago) of the central Austroalpine of Grisons, Switzerland. It had a wingspan of 4.41 feet. It has been debated whether it was a piscivore or omnivore.